羅椀升 (Dr. Wan-Sheng Sunny Lo)
- 博士 美國聖若望大學生物學系
研究領域:
本實驗室的研究重點在於了解細胞生長分化的過程中,染色質結構變化之原因及其對基因調控之作用。我們利用酵母菌及阿拉伯芥作為實驗的材料,探討表觀遺傳學及基因調控之分子機制。研究主題有二:
一. 組蛋白修飾對染色質結構、基因表達及基因組穩定性之調控機制
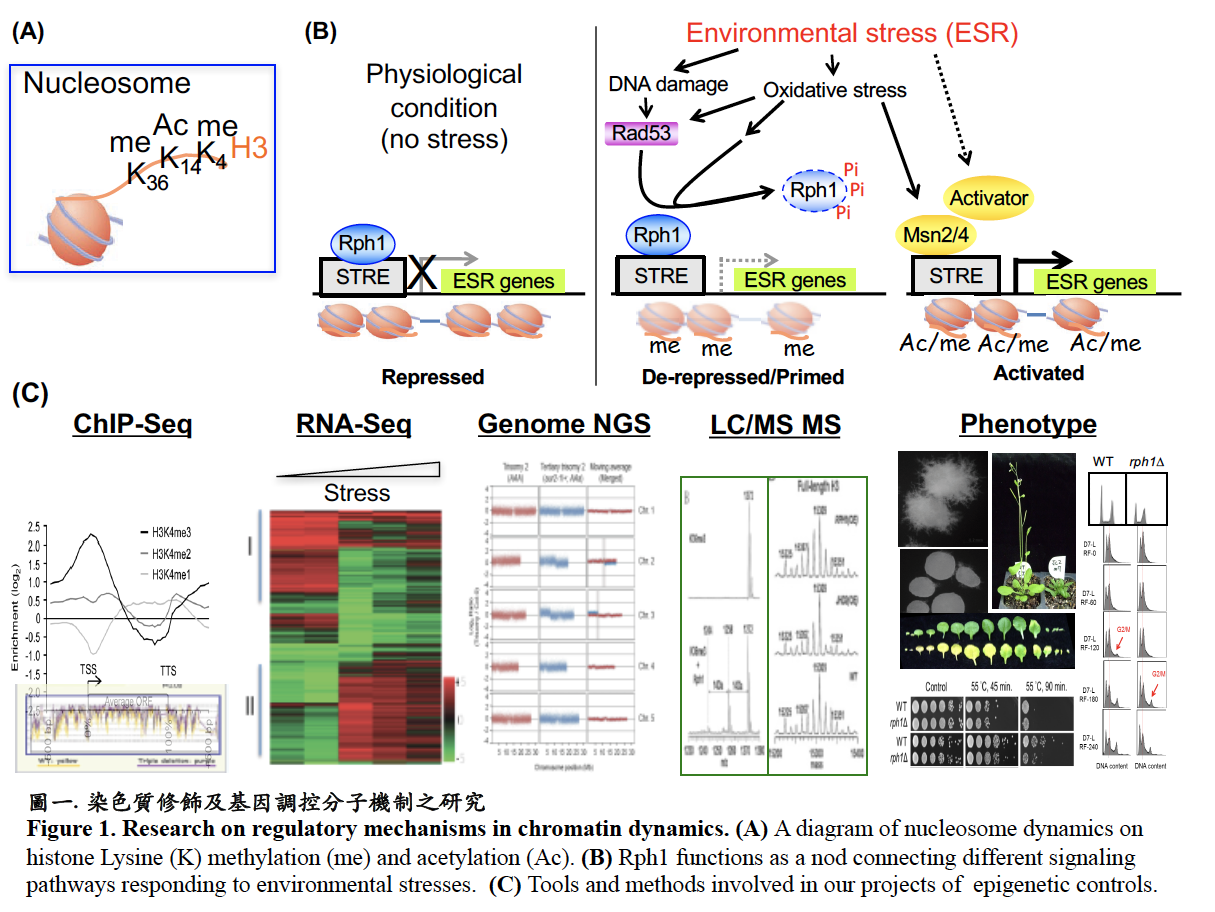
染色質修飾在調控基因轉錄扮演重要的角色。我們致力於探討去甲基酶複合體活性及組蛋白修飾的改變對於活化基因之影響及調控機制。利用基因體學,蛋白質體學及代謝體學等方法,我們發現H3K3去甲基酶(ScRph1)可藉由蛋白質磷酸化和表現量調控其與染色質結合並抑制基因轉錄,進而調節標的基因表達,適切反應不同環境所需的生理功能而達到細胞生長與老化的平衡。而H3K4去甲基酶(ScJhd2)具有阻絕不同區域染色質結構的活性及控制非編碼RNA的表現,參與調控異染色質之基因靜默及菌絲生長。此外,我們發現阿拉伯芥的H3K4去甲基酶(AtJP1)參與幼苗綠化發育及黑暗誘導葉片老化的過程。我們將持續研究去甲基酶在細胞老化之調控機制,藉由分析逆境及老化相關的基因表現,瞭解細胞老化的過程。同時,我們也將探討染色質修飾如何調節植物生長發育和適應環境逆境的分子機制。(圖一)
二. 研究真菌菌絲發育及篩選抗真菌之新穎化合物
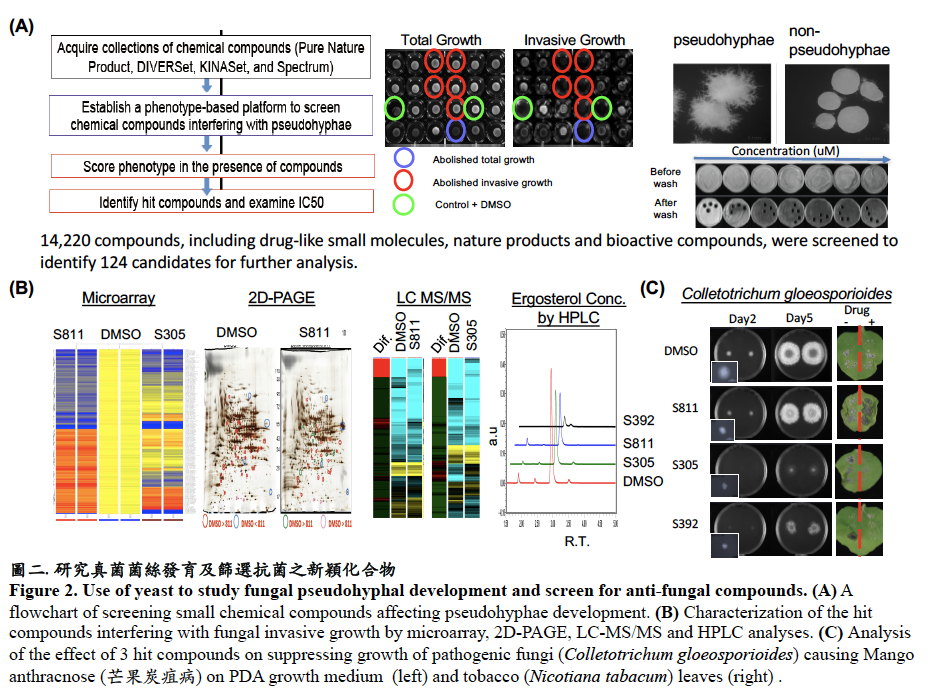
研究真菌致病機制及開發抗菌新標靶藥物,為防治真菌感染之重要課題。我們利用以酵母菌建立的藥物篩選平台,已得到多種抑制假性菌絲形成的小分子化合物。目前以分子遺傳學、化學遺傳學、蛋白質體學及基因晶片等方法,進行小分子化合物抑菌機制之研究。預期本研究之成果可增進對真菌致病及抗藥機制的了解,亦有助於研發治療人類與動植物真菌感染之藥物。(圖二)
- Wang LC, Montalvo-Munoz F, Tsai YC, Liang CY, Chang CC, Lo WS*. (2015) The histone acetyltransferase, Gcn5, regulates ncRNA-ICR1 and FLO11expression for pseudohyphal development in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BioMed Research International doi:10.1155/2015/284692
- Catinot J, Huang JB, Huang PY, Tseng MY, Chen YL, Gu SY, Lo WS, Wang LC, Chen YR, Zimmerli L*. (2015) ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 96 positively regulates Arabidopsis resistance to necrotrophic pathogens by direct binding to GCC elements of jasmonate - and ethylene-responsive defence genes. Plant, Cell and Environment doi:10.1111/pce.12583
- Lo KL, Wang LC, Chen IJ, Liu YC, Chung MC and Lo WS* (2014) Transcriptional consequence and impaired gametogenesis with high-grade aneuploidy in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114617.
- Liang CY, Wang LC, Lo WS * (2013) Dissociation of the H3K36 demethylase Rph1 from chromatin mediates derepression of environmental stress-response genes under genotoxic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular Biology of the Cell 24(20):3251-3262.
- Chen IJ, Lo WS, Chuang JY, Cheuh CM, Fan YS, Lin YC, Wu SJ, Wang LC* (2013) Chemical genetics reveals a role of brassinolides and cellulose synthase in the hypocotyl development of etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Science 209: 46-57.
- Liang CY, Hsu PH, Chou DF, Pan CY, Wang LC, Huang WC, Tsai MD, Lo WS * (2011) The histone H3K36 demethylase Rph1/KDM4 regulates the expression of the photoreactivation gene PHR1. Nucleic Acids Research. 39(10): 4151-4165.
- Tu S, E. Bulloch MM, Yang L, Ren C, Huang WC, Hsu PH., CH Chen CH, Liao CL, Yu HM, Lo WS *, Freitas MA*, Tsai MD* (2007) Identification of histone demethylases in Sacchromyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 282(19): 14262-71
- Nayak V, Zhao K, Wyce A, Schwartz MF, Lo WS, Berger SL, Marmorstein R* (2006) Structure and dimerization of the kinase domain from yeast Snf1, a member of the Snf1/AMPK protein family. Structure 14(3): 477-485.
- Lo WS, Gamache ER, Harry KW, Yang D, Pillus L and Berger SL* (2005) Activator-targeted Snf1-mediated histone H3 phosphorylation promotes TBP recruitment through distinct promoter-specific mechanisms. EMBO J. 24:997-1008
- Lo WS, Henry KW, Schwartz MF and Berger SL* (2004) Histone modification patterns during gene activation. Method in Enzymology 377:130-153
- Clements A, Poux AN, Lo WS, Pillus L, Berger SL, and Marmorstein R* (2003) Structural basis for histone and phospho-histone binding by the GCN5 histone acetyltransferase. Molecular Cell, 12(2):461-473
- Henry KW, Wyce A, Lo WS, Duggan LJ, Emre NCT, Kao CF, Pillus L, Osley MA and Berger SL* (2003) H2B ubiquitylation and deubiquitylation through the SAGA-associated hydrolase Ubp8 are both required for transcriptional activation. Gene & Dev., 17(21):2648-2663
- Lo WS, Duggan LJ, Belotserkovskya R, Emre NCT, Lane W, Shiekhattar R, and Berger SL* (2001) Snf1 is a histone kinase which works in concert with the histone acetyltransferase Gcn5 to regulate transcription. Science, 293:1142-1146.
- Lo WS, Trievel RC, Rojas JR, Duggan L, Hsu JY, Allis CD, Marmorstein R and Berger SL* (2000) Phosphorylation of Serine 10 in Histone H3 Is Functionally Linked In Vitro and In Vivo to Gcn5-Mediated Acetylation at Lysine 14. Molecular Cell 5(6): 917-926.

