[Lay-Sun Ma] Molecular Puppeteering: Roles of Ustilago maydis Effectors.
POST: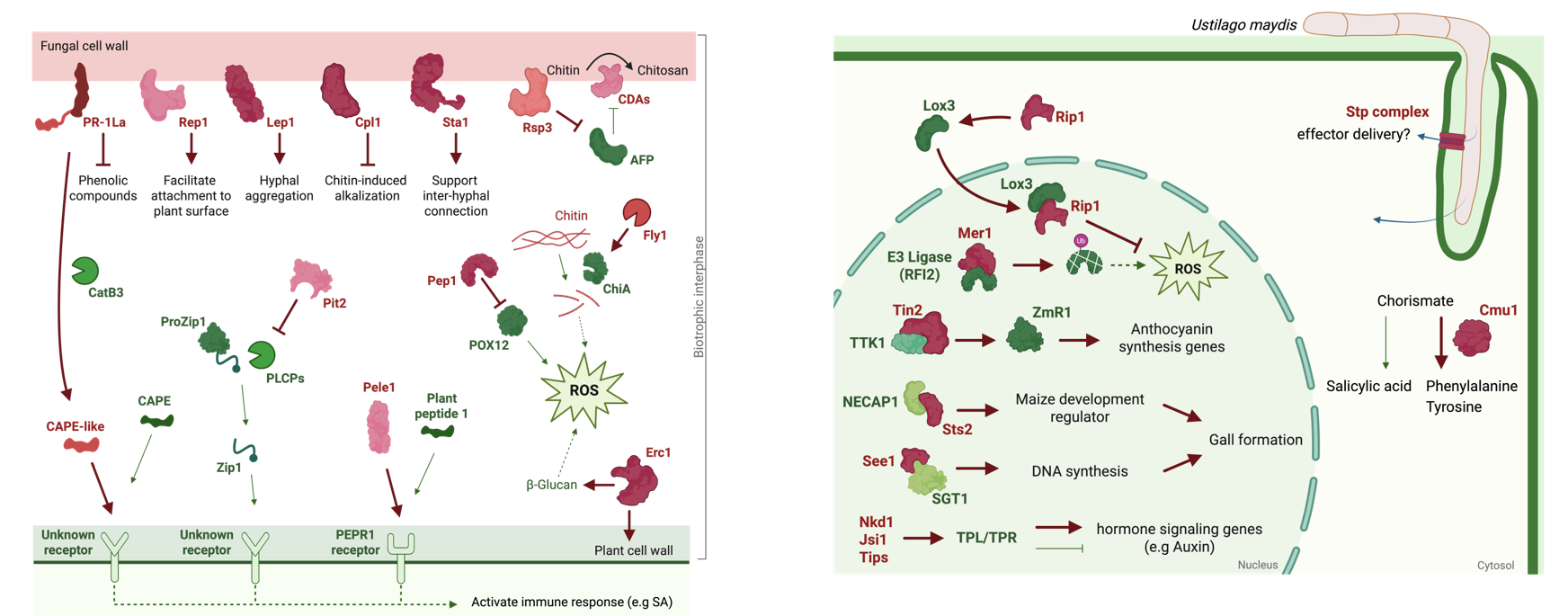
Versatile Strategies of U. maydis effectors: Wall-Associated and Apoplastic-localized Effectors in Overcoming Maize Apoplastic Defenses (Left). Translocated effectors in reprogramming host physiological processes (Right).
Effector proteins are central to the pathogenicity of filamentous fungi, particularly in smut fungi like Ustilago maydis, where impaired delivery of effectors into host cells results in attenuated virulence. This review outlines how U. maydis effectors function across diverse host compartments to manipulate host responses and induce tumor-like gall formation. We explore how effector studies uncover novel aspects of plant defense and highlight the evolutionary divergence between core and accessory effectors, shaped by host adaptation and selective pressure. Despite recent advances, challenges remain in characterizing poorly conserved or intrinsically disordered effectors. We emphasize the need for species-specific functional validation and improved tools, such as structural modeling, localization strategies, and maize genetic manipulation. Integrating structural and functional approaches will be essential to decipher effector mechanisms and the molecular arms race between smut fungi and their hosts, ultimately informing strategies for durable crop resistance.