[Pao-Yang Chen] Lignocellulose degradation in bacteria and fungi: cellulosomes and industrial relevance
POST: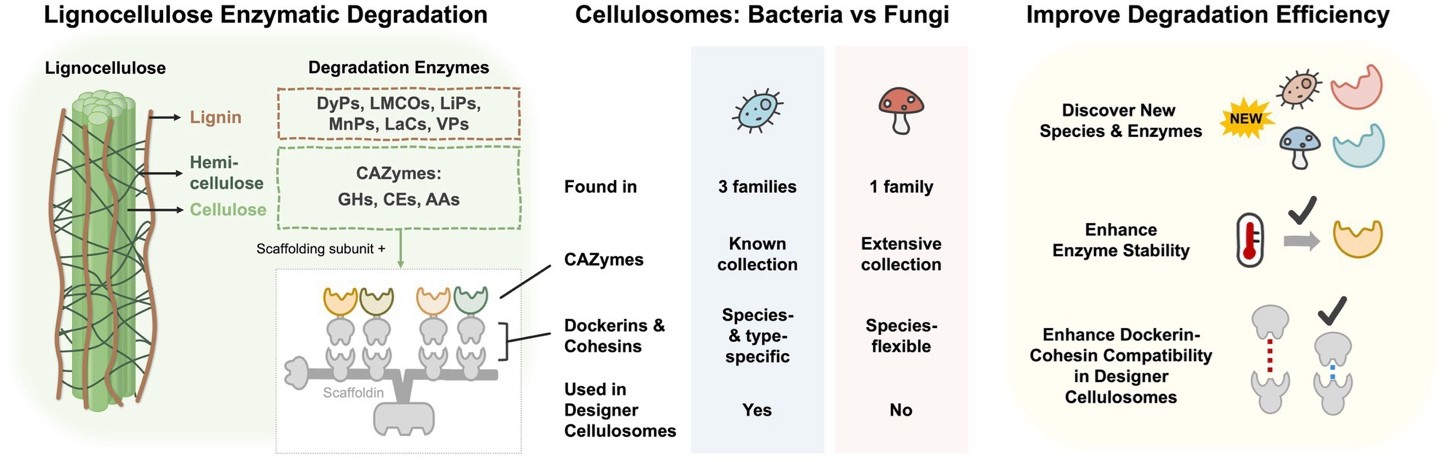
Graphical Abstract. Overview of lignocellulose enzymatic degradation in bacteria and fungi. The left panel illustrates the enzymes involved in lignocellulose breakdown. The cellulosome is a multi-enzyme complex composed of various CAZymes and a structural scaffold subunit that includes scaffoldins, dockerins, cohesins, and carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs). The middle panel highlights structural differences between bacterial and fungal cellulosomes. The right panel presents potential strategies to enhance lignocellulose degradation efficiency.
Lignocellulose is a plant-based material and one of the most common sources for making sustainable biofuels. However, turning it into fuel on a large scale is still difficult. One of the main problems is that the enzymes used to break it down are expensive and not efficient enough. To solve this, researchers are exploring better ways to make these enzymes work faster and cost less. One promising idea is to build enzyme complexes similar to those found in bacteria, called cellulosomes. These natural systems can greatly improve the breakdown of plant material—up to 50 times better than using enzymes alone. But the synthetic versions of these complexes are still unstable and less effective than natural ones. In this review, we look at current knowledge in three areas: (1) the types of enzymes bacteria and fungi use to break down lignocellulose; (2) how cellulosomes work in both systems and how they might be improved through engineering; and (3) three strategies to boost enzyme performance - finding new microbes and enzymes, making enzymes more heat-resistant, and designing better enzyme complexes. These findings could help develop cleaner, more efficient ways to turn plant waste into renewable energy.
This article was published in Frontiers in Microbiology and was kindly supported by funding from Academia Sinica.