[Yuki Nakamura] More than a membrane component: critical role of phospho-base methyltransferases for phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and plant development
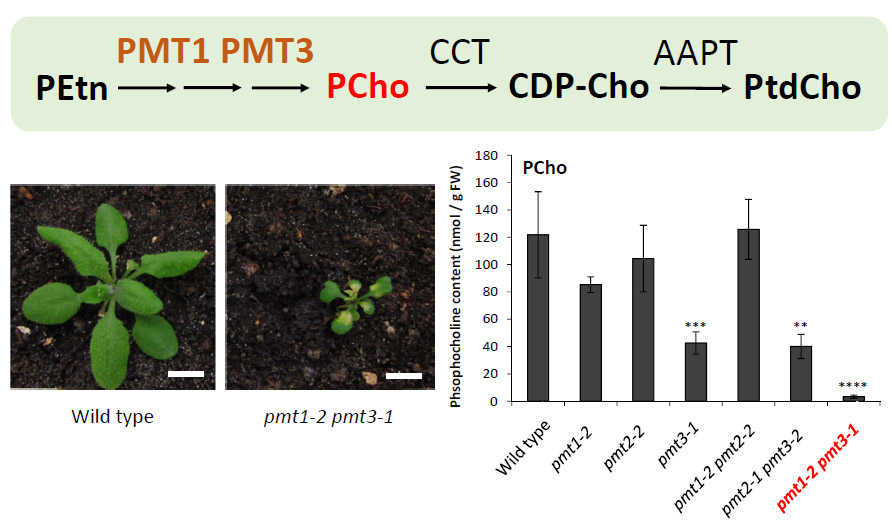
POST:Phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) is the conserved membrane lipid component among eukaryotic cells yet playing multiple biological roles beyond a constituent of cellular membranes. In plants, the phospho-base N-methyltransferases (PMTs) catalyze the biosynthesis of phosphocholine (PCho), a prerequisite for PtdCho biosynthesis. However, it remains elusive whether specific PMT isoform is involved in PtdCho biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. A research project led by Dr. Yuki Nakamura revealed that two isoforms of PMT, PMT1 and PMT3, redundantly play an essential role in PCho biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Double mutation of PMT1 and PMT3 contained trace amount of PCho and affected PtdCho biosynthesis in vivo, showing severe growth defect due to defective leaf vein patterning. This study highlights the importance of PMT1 and PMT3 in PCho biosynthesis, which are required for PtdCho biosynthesis, and possible roles of these metabolites in vascular development in Arabidopsis.