[Pao-Yang Chen] Dynamics of the Methylome and Transcriptome during the Regeneration of Rice
POST:Figure: Methylome and transcriptome analysis during rice regeneration.
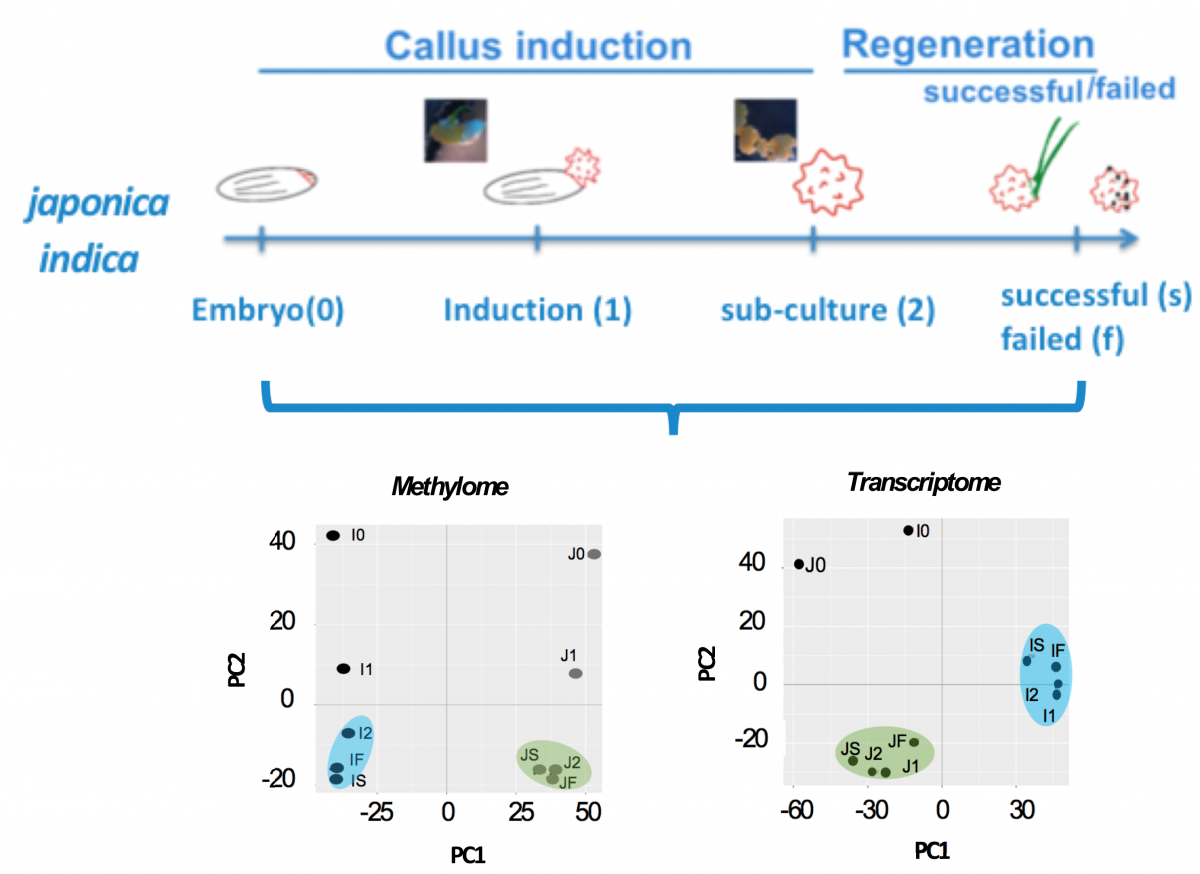
We collected embryo, callus (induction, subculture), failed and successful regenerants from japonica and indica rice, and performs whole genome bisulfite sequencing and RNA-seq. From the analysis we see significant cluster in methylome and transcriptome based on cultivars, suggesting DNA methylation might be a factor of impacting the efficiency of rice regeneration.
Oryza sativa indica (cv. IR64) and Oryza sativa japonica (cv. TNG67) vary in their regeneration efficiency. Such variation may occur in response to cultural environments that induce somaclonal variation. Somaclonal variations may arise from epigenetic factors, such as DNA methylation. We hypothesized that somaclonal variation may be associated with the differential regeneration efficiency between IR64 and TNG67 through changes in DNA methylation. We generated the stage-associated methylome and transcriptome profiles of the embryo, induced calli, sub-cultured calli, and regenerated calli (including both successful and failed regeneration) of IR64 and TNG67. We found that stage-associated changes are evident by the increase in the cytosine methylation of all contexts upon induction and decline upon regeneration. These changes in the methylome are largely random, but a few regions are consistently targeted at the later stages of culture. The expression profiles showed a dominant tissue-specific difference between the embryo and the calli. A prominent cultivar-associated divide in the global methylation pattern was observed, and a subset of cultivar-associated differentially methylated regions also showed stage-associated changes, implying a close association between differential methylation and the regeneration programs of these two rice cultivars. Based on these findings, we speculate that the differential epigenetic regulation of stress response and developmental pathways may be coupled with genetic differences, ultimately leading to differential regeneration efficiency. The present study elucidates the impact of tissue culture on callus formation and delineates the impact of stage and cultivar to determine the dynamics of the methylome and transcriptome in culture.