[Ting-Ying Wu] Modeling alternative translation initiation sites in plants reveals evolutionarily conserved cis-regulatory codes in eukaryotes
POST: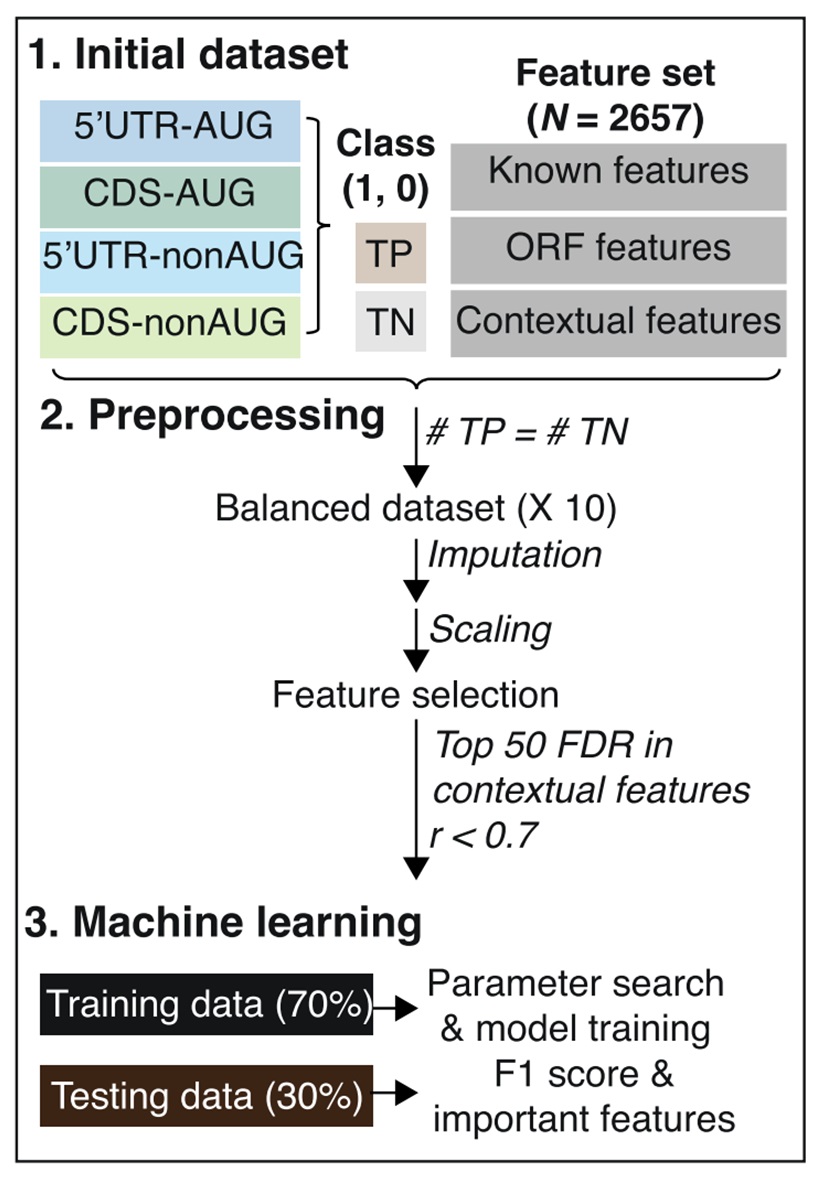
Identification of prediction models and the associated features that predict plant alternative translation initiation sites (TISs). Machine-learning (ML) workflow used to identify prediction models and the features that were informative for predicting TISs.
mRNA translation relies on identifying translation initiation sites (TISs) in mRNAs. Alternative TISs are prevalent across plant transcriptomes, but the mechanisms for their recognition are unclear. Using ribosome profiling and machine learning, we developed models for predicting alternative TISs in the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Distinct feature sets were predictive of AUG and nonAUG TISs in 5′ untranslated regions and coding sequences, including a novel CU-rich sequence that promoted plant TIS activity, a translational enhancer found across dicots and monocots, and humans and viruses. Our results elucidate the mechanistic and evolutionary basis of TIS recognition, whereby cis-regulatory RNA signatures affect start site selection. The TIS prediction model provides global estimates of TISs to discover neglected protein-coding genes across plant genomes. The prevalence of cis-regulatory signatures across plant species, humans, and viruses suggests their broad and critical roles in reprogramming the translational landscape.